
This explanation is also available in Italian language and and is here.
Home automation is a very large topic that takes a long time to be analyzed in detail.
Here we will give the basic ideas from which then to start to deepen.
In general, home automation is used to simplify and automate the main activities carried out in the home, office, etc.
A good home automation system is one that is not noticed because it does not require particular activities from the user.
A home automation system must be reliable and must be able to operate autonomously without the need to connect to the Internet to carry out actions such as switching lights on/off, irrigation control, etc.
A home automation system can include numerous features such as light control, irrigation, heating, air conditioning, anti-theft and much more.
If we are building a house the best thing (in terms of safety) is to provide wiring for the various systems that we are going to control.
This solution is the safest but it is also the most expensive due to the kilometers of cables that must be installed.
An alternative solution is to use a wireless system that is able to give us the right security and is able to cover our entire home.
The types of wireless communications that can be chosen are:
- Sub1Ghz – long distances, low consumption, low amount of data
- WiFi – short/medium distances, high consumption, very high amount of data
- BlueTooth – short distances, low consumption, medium-high amount of data
- ZigBee – theoretically infinite distances (Mesh 3.0), low power consumption, low amount of data
More details on the networks mentioned above can be found here while for the Sub1Ghz you can find them here.
From the above it is practically mandatory to choose ZigBee systems for the considerable distances that can be covered thanks to the Mesh but if you also want to use cameras (here the amount of data to be transmitted is considerable) then it will be necessary to use a second network that uses the Wifi.
NOTE about ZigBee Mesh (ZBM)
A ZBM network is basically composed of the nodes shown below.
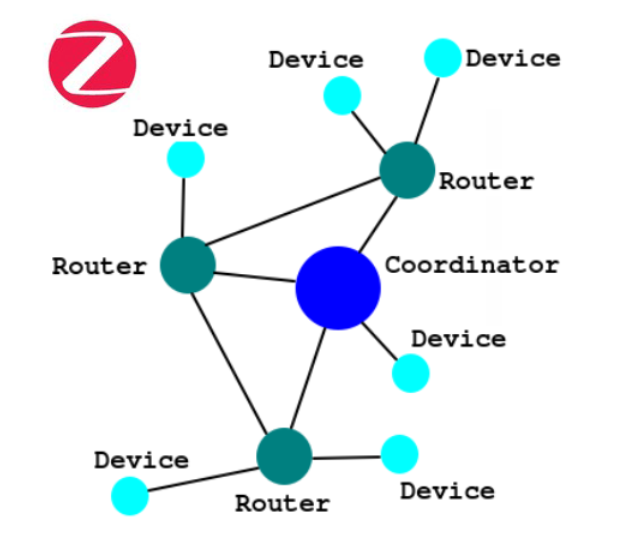
- Coordinator is the module that manages the entire ZBM network,
- Routers are all those objects that in addition to performing their function (for example light bulbs) also repeat the signals of the Devices if the latter cannot speak directly with the Coordinator.
- Devices are normally door / window sensors, temperature / humidity sensors, etc.These, being normally powered by a battery, are connected either directly to the Coordinator or to a Router which will then retransmit the data to the Coordinator.
More details about the ZBM can be found here.
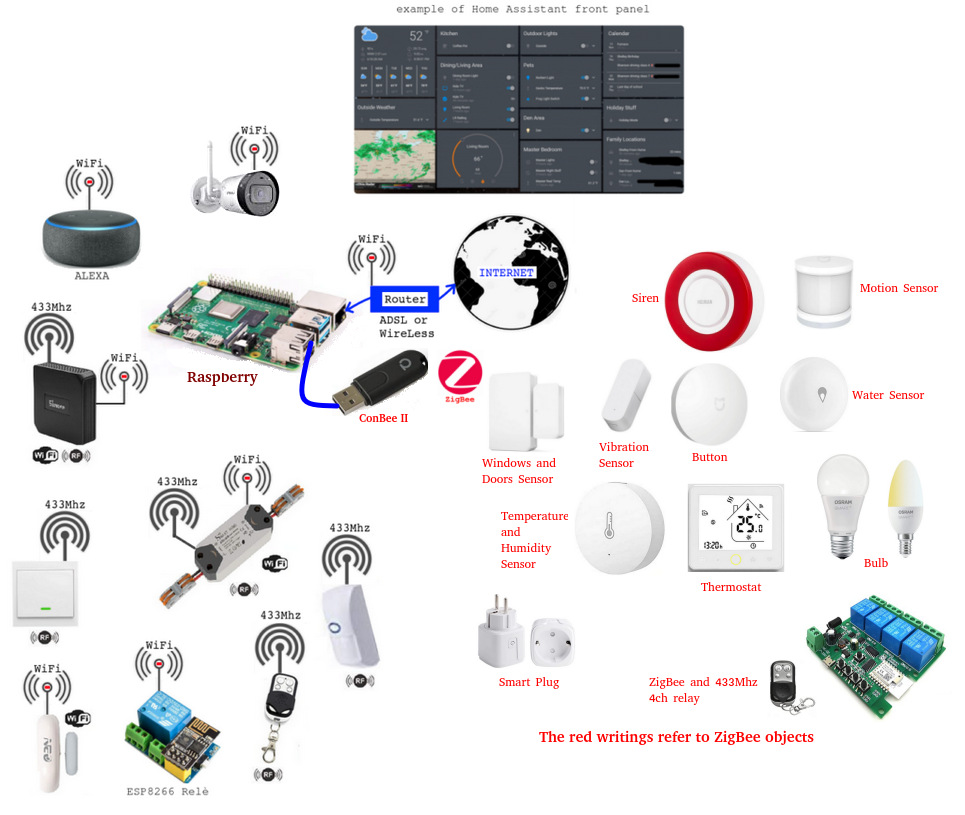
Since our home automation system will consist of sensors, lamps, actuators and cameras, our wireless home automation network will exploit two technologies which are:
ZigBee
Wifi
As we said at the beginning, we want our home automation system to work even without having a continuous connection to the Internet and we also want to integrate smart objects that we have purchased over the years.
The ideal solution is to use Home Assistant installed on a Raspberry PI 4 Model B 4GB.
Home Assistant is free and compatible with thousands of smat systems (lamps, actuators, air conditioners, cleaning robots, etc.) and can be installed on different platforms ranging from Linux to Windows to Raspberry.
Obviously Home Assistant must always remain on so we opted to install it on Raspberry whose suggested kit you can see here.
Since we also have to manage a ZigBee network, we suggest the use of the ConBee II key which is a universal USB gateway for Zigbee, more details can be found here.
For the management of the cameras we will obviously use the home WiFi network, perhaps with the use of some signal repeater, see for example here and here.
Our hypothetical network will look like this below.
Last but not least we should take care of the power supply of the Raspberry and also of the home ROUTER so as to guarantee at least the working ZigBee network.
This is to ensure that even in the absence of power supply (220 Vac) our network works, in this regard we suggest to power the Raspberry and the ROUTER with a UPS of at least 1000 VA, here you will find different models.
In particular, we have been using the 1500 VA model for more than a year now and during the lack of 220 Vac (missing for more than an hour) it held up very well the power supply for the Raspberry and the ROUTER.
When you have installed your Home Assistant then you will have to create your AUTOMATIONS that are a sequence of commands that using your sensors, buttons, etc., and are able to perform actions in complete autonomy.
For example, when entering the house in the evening and / or at night, the entrance lights must be switched on automatically.
Remember that automation can only be said to be perfect if it works exactly as we want it without uncertainty and is reliable over time. Translated, when you write an automation, you must spends all time is necessary to test it in detail in order to avoid unpleasant unforeseen consequences.
Think of an automation for irrigating that does not shut off the water when expected or that irrigates even while it is raining.
Last but not least, automation is all the more appreciated the more it manages to automate activities without getting noticed.
Obviously, Home Assistant can also be accessed from outside the home through a mobile phone, tablet or PC so as to give you the ability to control what is happening in your home.
For more details see here.
