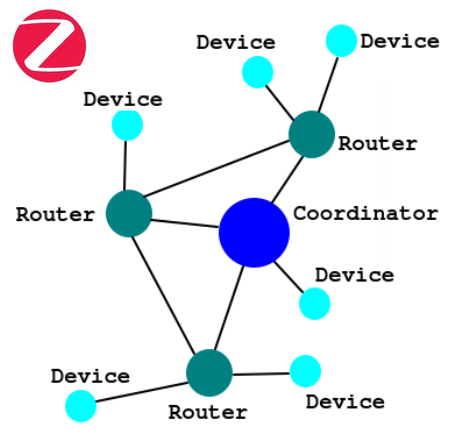
Above there is a representation of the ZigBee Mesh Network.
ZigBee is a wireless technology developed as an open global standard to address the unique needs of low-cost, low-power wireless IoT networks.
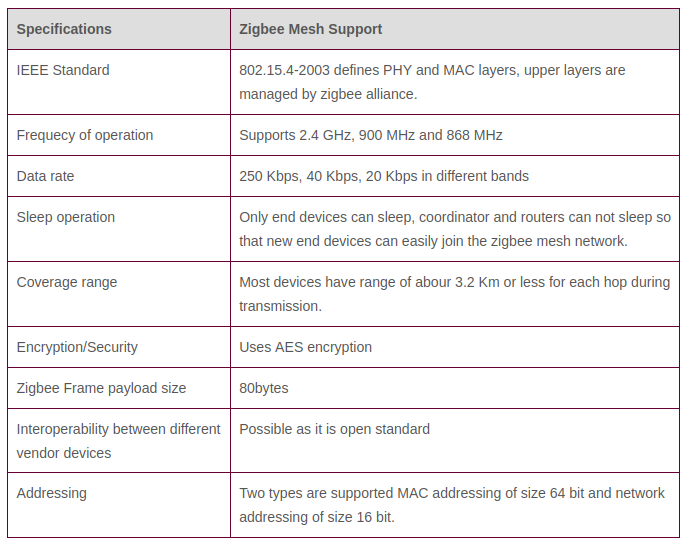
The ZigBee standard operates on the IEEE 802.15.4 physical radio specification and operates in unlicensed bands including 2.4 GHz, 900 MHz and 868 MHz.
- Zigbee protocol features include:
- Support for multiple network topologies such as point-to-point,
- point-to-multipoint and mesh networks
- Low duty cycle – provides long battery life
- Low latency
- Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
- Up to 65000 nodes per network
- 128-bit AES encryption for secure data connections
- Collision avoidance, retries and acknowledgements
ZigBee include also the mesh network layer, each node relays or routes data till it reaches the destination node.
Mesh networking is very powerful in routing the data.
In mesh, each of the nodes co-operate with other nodes so that equal distribution of data can be achieved.
The ZigBee mesh network (ver.3.0) is excellent for creating automation systems thanks to the very low latency of the devices.
For example see our Home Assistant and our selection of ZiGBee devices.
The main advantages of the mesh network are the following:
- The distances covered by the COORDINATOR to the last DEVICE can be considerable as it allows data to pass from one node to another
- Bringing any node into the network is easy
- The network is self-healing because in the event of a node failure or lost connection conditions, data can be routed through other healthy nodes on the network.
- Zigbee is open standard and hence interoperability between different vendor devices can be done without any issues.
We use in the same network the following components and the Coordinator is ConBee II in Home Assistant:
NOTE
We have noticed, during real test, that is quite a must use devices declared Zigbee 3.0 compliant to avoid problems in Mesh Network.
Description of Coordinator, Routers and Devices
- Only one Coordinator is needed to form zigbee network.
The coordinator stores all the critical information about the zigbee network including encryption keys and can also connect directly the devices. - Routers are intermediate nodes which help in relaying data between devices.
Often the bulbs also do the double role of router and device. - Devices are of two types:
- Reduced function devices and Full function devices.
- Reduced function devices can not relay data and will talk to their parent devices (routers/coordinator) to perform relaying. On the other end, full function devices do the job of relaying.
Following are the principles features of Zigbee Mesh network.
REMEMBER
ZigBee Mesh has been developed to support low data rate and low power applications.
ZigBee 3.0
The standard ZigBee 3.0 is variation to previous ZigBee standards.
The ZigBee 3.0 specification enables interoperability among different application profiles.
Due to this, ZigBee 3.0 allows devices from different application areas to communicate and form single homogeneous network.
For example, device_1 from ZigBee light profile can coexist with device_2 from health care profile with same ZigBee network.
Moreover ZigBee 3.0 compliant devices support connectivity with IP networks such as LAN and WAN. Hence these devices can form IoT network.
Hence products from different manufacturers can communicate together as single networking devices.
ZigBee 3.0 is based on IEEE 802.15.4 standard specifications and support 2.4 GHz global frequency band. It uses ZigBee PRO version.
(by: rfwireless-world.com)
The principal features of zigbee 3.0 are:
- Low Power
- Reliable and Robust
- Scalable
- Secure
- Large number of nodes about 250/65000
- Rejoining of orphaned nodes with the new parent node in the event of loss of parent
- Global Standard
- ZigBee 3.0 provides backward compatibility with other ZigBee application profiles such as ZigBee light link 1.0 profile, ZigBee home automation 1.2 profile etc.
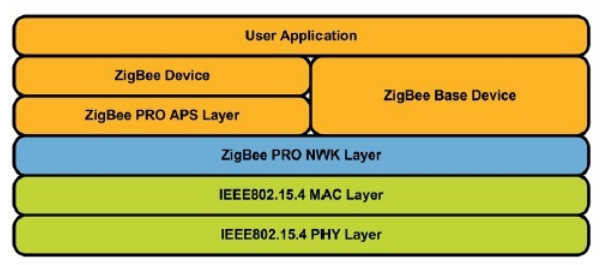
Zigbee 3.0 Protocol Stack
OTA
Zigbee’s Over-The-Air (OTA) upgrade feature for software updates during device operation ensures that applications on devices already deployed in the field can be seamlessly migrated to Zigbee 3.0.
OTA upgrade is an optional functionality that manufacturers are encouraged to support in their Zigbee products.
LINKs
- Comparison: ZigBee – WiFi – BlueTooth – UWB – see here
- Getting started with Zigbee on STM32WB Series (AN5506)
- Zigbee Wireless Mesh Networking
