
Introduction
Bluetooth (over IEEE 802.15.1), ultra-wideband (UWB, over IEEE 802.15.3), ZigBee (over IEEE 802.15.4), and Wi-Fi (over IEEE 802.11) are four protocol standards for short range wireless communications with low power consumption (2.4/5Ghz).
From an application point of view:
Bluetooth is intended for a cordless mouse, keyboard, and hands-free headset
UWB is oriented to high-bandwidth multimedia links
ZigBee is designed for reliable wirelessly networked monitoring and control networks
Wi-Fi is directed at computer to computer connections as an extension or substitution of cabled networks
reference: ResearchGate
More info are here:
A Comparative Study of Wireless Protocols: Bluetooth, UWB, ZigBee, and Wi-Fi
Some abstractions are below.
Main Features
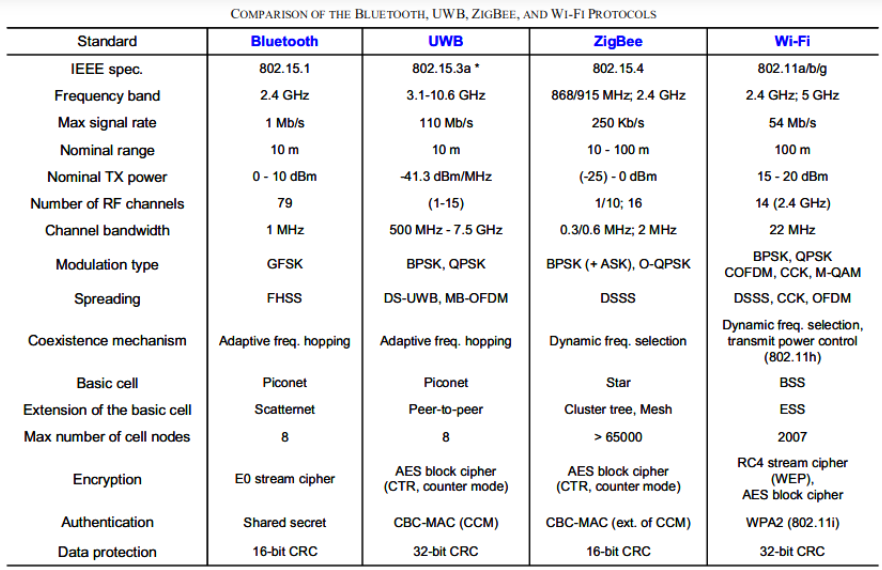

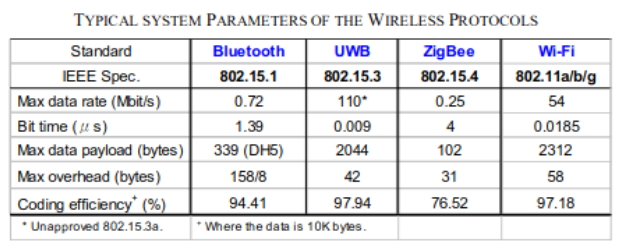
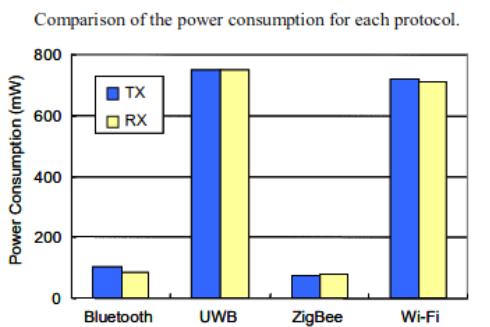
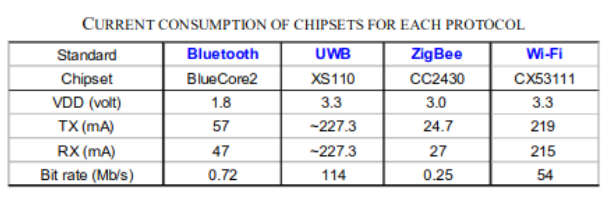
ZigBee
ZigBee over 802.15.4 protocol can meet a wider variety of real industrial needs, for example the long-term battery operation, greater useful range, flexibility in a number of dimensions, and reliability of the mesh networking architecture.
ZigBee provides self-organized, multi-hop, and reliable mesh networking with long battery lifetime.
The maximum number of devices belonging to the network’s building are over 65000 for a ZigBee mesh.
ZigBee devices can communicate with the next node in the network (repeater function – mesh): this ensures connection to a single central gateway hub even when it is not directly reachable from all the nodes in the network, see image below.
Beware that, however normally not all battery-powered ZigBee devices implement the repeater function (mesh) to save batteries, certainly all powered devices also work as repeaters (mesh).
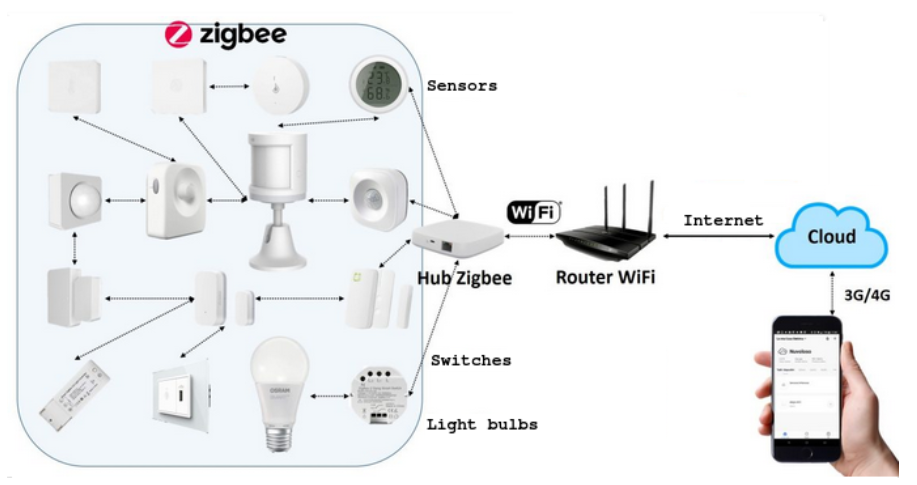
If you are interested in how to use the ZigBee in Home Assistant (hassio) look here.
LINK
See also the:
COMPARISON OF CHARACTERISTICS FOR DIFFERENT WIRELESS PROTOCOLS – Bluetooth, UWB, ZigBee/IP, Wi-Fi, Wi-Max, GSM/GPRS
